- Published at
Vite + React + TS + FFmpeg WASM

使用ffmpeg.wasm與React製作一個轉檔程式
- Authors
-
-

- Name
- Zup
-
Table of Contents
初始化專案
新增一個專案
pnpm create vite@latest
選擇React之後,專案建立完成。
接著設定TailwindCSS,根據官網的指引,安裝套件並初始化
pnpm add -D tailwindcss postcss autoprefixer
pnpm dlx tailwindcss init -p
(溫馨提醒,這裡的npx是對應pnpm dlx,但有時不能直接這樣交換)
安裝好後,因為想要在所有元件裡面使用,因此去tailwind.config.js修改content欄位
/** @type {import('tailwindcss').Config} */
export default {
content: [
// content原本是空的,把這些加進去
"./index.html",
"./src/**/*.{js,ts,jsx,tsx}",
],
theme: {
extend: {},
},
plugins: [],
};
接著,去掉新增專案時所有生成的css,index.css寫上這三行
@tailwind base;
@tailwind components;
@tailwind utilities;
(我也把App.css裡面全部清空了)
接著開啟dev server,如果看到樣式全部跑掉,就代表成功了。
安裝ffmpeg.wasm
使用套件管理器安裝
pnpm add @ffmpeg/ffmpeg @ffmpeg/util
在開始coding前,先調整一下vite的設定檔,讓ffmpeg可以正常運作。
vite.config.ts
import { defineConfig } from "vite";
import react from "@vitejs/plugin-react";
// https://vitejs.dev/config/
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [react()],
optimizeDeps: {
exclude: ["@ffmpeg/ffmpeg", "@ffmpeg/util"],
},
server: {
headers: {
"Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy": "same-origin",
"Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy": "require-corp",
},
},
});
在使用前,必須要先把ffmpeg.wasm從網路上下載到你的電腦裡。因為這個檔案很大,20幾MB,所以才需要做這些額外的loading。
import { useEffect, useRef, useState } from "react";
import { FFmpeg } from "@ffmpeg/ffmpeg";
import "./App.css";
import { toBlobURL } from "@ffmpeg/util";
function App() {
const ffmpegRef = useRef(new FFmpeg());
const messageRef = useRef<HTMLParagraphElement | null>(null);
const [isFFmpegLoading, setIsFFmpegLoading] = useState(true);
useEffect(() => {
const loader = async () => {
const baseURL = "https://unpkg.com/@ffmpeg/core@0.12.6/dist/esm";
const ffmpeg = ffmpegRef.current;
ffmpeg.on("log", ({ message }) => {
if (messageRef.current) messageRef.current.innerHTML = message;
});
await ffmpeg.load({
coreURL: await toBlobURL(
`${baseURL}/ffmpeg-core.js`,
"text/javascript"
),
wasmURL: await toBlobURL(
`${baseURL}/ffmpeg-core.wasm`,
"application/wasm"
),
});
setIsFFmpegLoading(false);
};
loader();
}, []);
if (isFFmpegLoading) {
return "loading";
}
return (
<>
{/*利用TailwindCSS 將畫面份為左右兩半 // 左邊輸入,右邊輸出*/}
<main className="grid h-screen w-screen grid-cols-2 bg-slate-700 p-2">
<div className="flex flex-col gap-2"></div> {/* 輸入 */}
<div className="flex flex-col gap-2"></div> {/* 輸出 */}
</main>
</>
);
}
export default App;
裡面好像加了些沒有講過的東西…別急,一個個慢慢來。
首先先來看最上層這幾個useState、useRef宣告
const ffmpegRef = useRef(new FFmpeg());
const messageRef = useRef<HTMLParagraphElement | null>(null);
const [isFFmpegLoading, setIsFFmpegLoading] = useState(true);
第一個是FFmpeg的Ref Object,因為React會針對畫面每一次渲染重新建立函數、物件,透過useRef Hook就能保持最一開始的樣子,不會重複建立。
第二個與轉檔時的文字有關。FFmpeg支援將log message輸出,這樣子在過程中就可以即時查看處理的狀態。
第三航的useState很單純,就只是確保當FFmpeg完成載入時,才顯示畫面。
到此為止,基礎設定就用好了,接下來要來處理檔案輸入、預覽與轉換完池後要怎麼顯示、下載的問題。
輸入影片檔
策略:利用<input />將影片檔輸入,用useState存起來,再丟給ffmpeg.wasm處理。
不過在那之前,也做一下輸入影片預覽,至少在轉換時可以看影片轉移注意力。
const [inputVid, setInputVid] = useState<File | null>(null);
function handleInput(e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) {
const file = e.target.files ? e.target.files[0] : null;
if (file) {
setInputVid(file);
}
}
return (
<main className="grid h-screen w-screen grid-cols-2 gap-2 bg-slate-700 p-2 text-white">
{/* 輸入 */}
<div className="flex flex-col gap-2">
<h1 className="border-b-2 border-white py-2 text-center font-mono text-3xl">
Input
</h1>
<input type="file" accept="video/*" onChange={handleInput} />
{inputVid && (
<>
<video controls>
<source src={URL.createObjectURL(inputVid)} />
</video>
<button className="rounded-md border-2 border-white px-3 py-2 text-white transition-all hover:bg-white hover:text-black">
Convert Video
</button>
<p ref={messageRef}></p> {/* FFmpeg運行時的log會呈現在這裡 */}
</>
)}
</div>
{/* 輸出 */}
<div className="flex flex-col gap-2">
<h1 className="border-b-2 border-white py-2 text-center font-mono text-3xl">
Output
</h1>
</div>
</main>
);
結果長這樣
Convert Video
成功把影片匯進來後,接著要把它交給FFmpeg去轉檔。
先來新增一個handle function,與處理完後的useState
const [outputVid, setOutputVid] = useState<string | null>(null);
// 你可能在想,為什麼輸入的`inputVid`型別為File,但這裡的`outputVid`卻是string?
async function handleConvert() {
if (!inputVid) {
return;
}
const ffmpeg = ffmpegRef.current;
await ffmpeg.writeFile("input.mp4", await fetchFile(inputVid));
await ffmpeg.exec(["-i", "input.mp4", "-c:v", "copy", "output.mp4"]);
const fileData = await ffmpeg.readFile("output.mp4");
const data = new Uint8Array(fileData as ArrayBuffer);
setOutputVid(
URL.createObjectURL(new Blob([data.buffer], { type: "video/mp4" }))
); // 因為在這裡就已經把檔案轉為ObjectURL,所以才是string
}
要展示也很簡單,由於已經轉為ObjectURL,因此就可以直接放進HTML Tag裡面的src屬性
{
outputVid && (
<>
<video controls>
<source src={outputVid} />
</video>
<a
href={outputVid} // See, ObjectURL 可以直接放入src裡面
className="rounded-md border-2 border-white px-3 py-2 text-center text-white transition-all hover:bg-white hover:text-slate-700"
target="_blank" // 按下download後,開新的視窗
>
Download
</a>
</>
);
}
影片轉檔通常需要花很多時間,不過完成以後,整個頁面看起來會像這樣
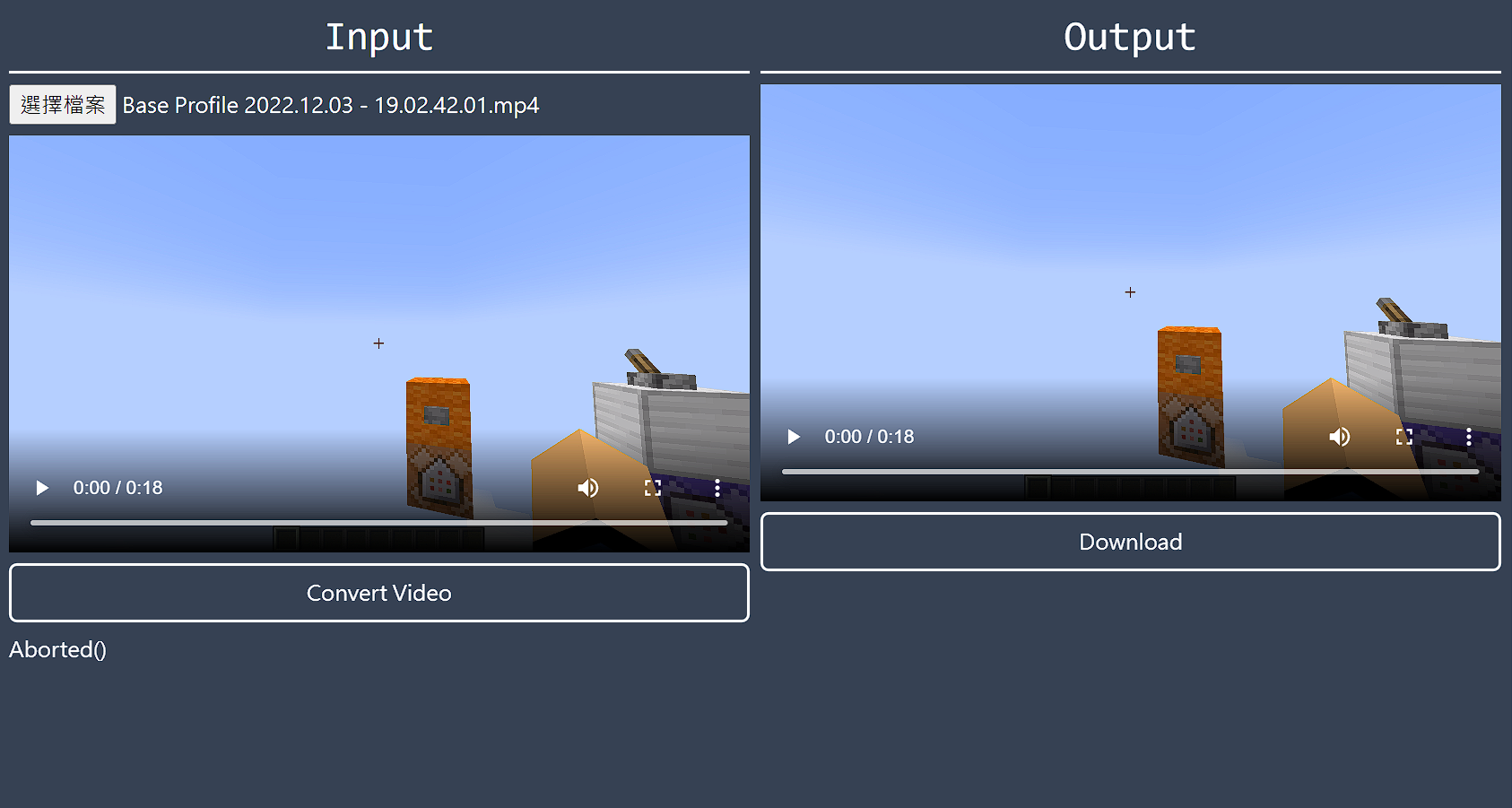
按一下download按鈕應該就能跳去新的頁面,either用瀏覽器撥放or開始下載。
code
import { useEffect, useRef, useState } from "react";
import { FFmpeg } from "@ffmpeg/ffmpeg";
import "./App.css";
import { fetchFile, toBlobURL } from "@ffmpeg/util";
function App() {
const ffmpegRef = useRef(new FFmpeg());
const messageRef = useRef<HTMLParagraphElement | null>(null);
const [isFFmpegLoading, setIsFFmpegLoading] = useState(true);
const [inputVid, setInputVid] = useState<File | null>(null);
const [outputVid, setOutputVid] = useState<string | null>(null);
const handleInput = (e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
const file = e.target.files ? e.target.files[0] : null;
if (file) {
setInputVid(file);
}
};
async function handleConvert() {
if (!inputVid) {
return;
}
const ffmpeg = ffmpegRef.current;
await ffmpeg.writeFile("input.mp4", await fetchFile(inputVid));
await ffmpeg.exec(["-i", "input.mp4", "output.mp4"]);
const fileData = await ffmpeg.readFile("output.mp4");
const data = new Uint8Array(fileData as ArrayBuffer);
setOutputVid(
URL.createObjectURL(new Blob([data.buffer], { type: "video/mp4" }))
);
}
useEffect(() => {
const loader = async () => {
const baseURL = "https://unpkg.com/@ffmpeg/core@0.12.6/dist/esm";
const ffmpeg = ffmpegRef.current;
ffmpeg.on("log", ({ message }) => {
if (messageRef.current) messageRef.current.innerHTML = message;
});
await ffmpeg.load({
coreURL: await toBlobURL(
`${baseURL}/ffmpeg-core.js`,
"text/javascript"
),
wasmURL: await toBlobURL(
`${baseURL}/ffmpeg-core.wasm`,
"application/wasm"
),
});
setIsFFmpegLoading(false);
};
loader();
}, []);
if (isFFmpegLoading) {
return "loading";
}
return (
<>
<main className="grid h-screen w-screen grid-cols-2 gap-2 bg-slate-700 p-2 text-white">
<div className="flex flex-col gap-2">
<h1 className="border-b-2 border-white py-2 text-center font-mono text-3xl">
Input
</h1>
<input type="file" accept="video/*" onChange={handleInput} />
{inputVid && (
<>
<video controls>
<source src={URL.createObjectURL(inputVid)} />
</video>
<button
onClick={handleConvert}
className="rounded-md border-2 border-white px-3 py-2 text-white transition-all hover:bg-white hover:text-black"
>
Convert Video
</button>
<p ref={messageRef}></p>
</>
)}
</div>
<div className="flex flex-col gap-2">
<h1 className="border-b-2 border-white py-2 text-center font-mono text-3xl">
Output
</h1>
{outputVid && (
<>
<video controls>
<source src={outputVid} />
</video>
<a
href={outputVid}
className="rounded-md border-2 border-white px-3 py-2 text-center text-white transition-all hover:bg-white hover:text-slate-700"
target="_blank"
>
Download
</a>
</>
)}
</div>
</main>
</>
);
}
export default App;
結尾
沒想到用ffmpeg.wasm也花了我一番力氣,因為官網提供的範本有些錯誤,原本在load()裡面還有包含workerURL,但現在去看檔案已經消失,所以我把這行給刪掉了。從來也沒想過官方的example會有問題。
Anyway,用ffmpeg.wasm轉影片檔的想法還是很不實際啦,就因為速度太慢了。不過小一點的音樂檔應該還行,單純將影格copy的簡單作業應該也可以,執行函數變成
await ffmpeg.exec(["-i", "input.mp4", "-c:v", "copy", "output.mp4"]);
-c:v代表影像的編碼方式,copy就是直接複製,不做任何處理。
WebAssembly, WASM的優點就是比Javascript快,不過因為種種的限制,不太可能真的取代JS,頂多就只是高計算場景下能起到加速的功能而已。不過有哪個Web App需要如此大量、誇張的Client Side Computing?屈指可數。